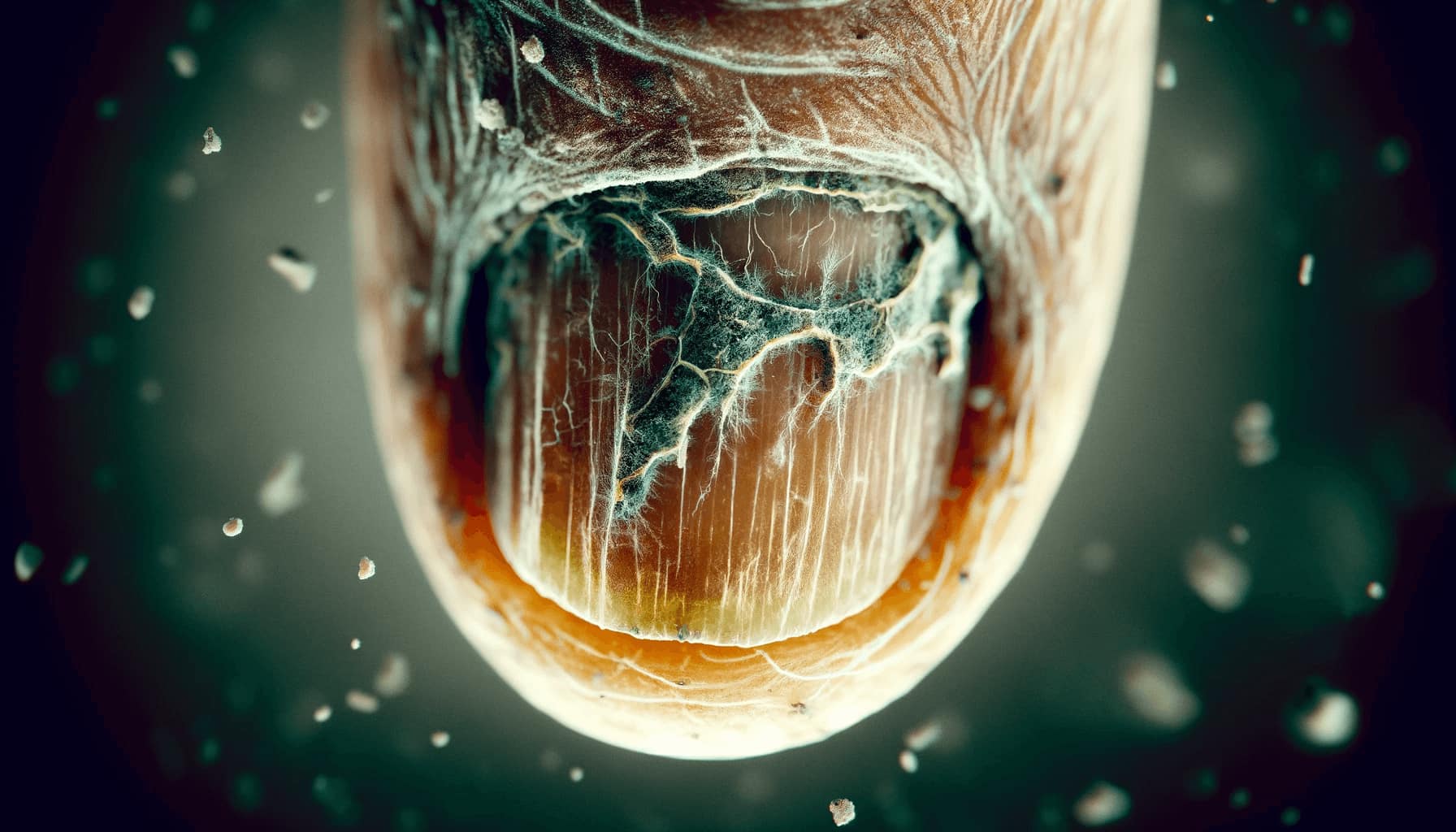
A nail fungal infection, medically known as onychomycosis, is a common condition that can affect both fingernails and toenails. This condition arises when a fungal organism, typically a dermatophyte, yeast, or mold, infects the nail. The infection can cause various symptoms, including nail discoloration, thickening, and brittleness. Understanding the causes of nail fungal infections is crucial for prevention and effective treatment.
Fungal Organisms and Their Proliferation
The primary cause of nail fungal infections is the overgrowth of fungi in, on, or under the nail. Fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, making the nails, especially the toenails, a prime target for infection. These organisms are microscopic and can invade through tiny cuts or separations between the nail and the nail bed.
Dermatophytes are the most common fungi responsible for nail fungal infections. These fungi primarily feed on keratin, a protein found in nails, hair, and skin. Other fungi, such as yeasts (Candida species) and molds, can also cause nail infections but are less common.
Risk Factors for Nail Fungal Infections
Several factors increase the risk of developing a nail fungal infection. These include:
- Age: Older individuals are more prone to fungal infections due to reduced blood circulation, slower nail growth, and longer exposure to fungi over their lifetime.
- Sweaty Feet: Excessive sweating creates a moist environment around the feet, ideal for fungal growth.
- History of Athlete’s Foot: Fungal infections of the skin, like athlete’s foot, can spread to the nails.
- Walking Barefoot in Damp Communal Areas: Places like gyms, swimming pools, and shower rooms are breeding grounds for fungi.
- Nail Injury or Nail Surgery: Damaged nails are more susceptible to fungal infections.
- Diabetes: People with diabetes have reduced blood circulation and immune responses, increasing the risk of fungal infections.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems, either from conditions like HIV/AIDS or from certain medications, are at a higher risk.
- Smoking: Smoking can affect circulation, increasing the risk of fungal infections.
Transmission of Fungal Infections
Fungal infections can spread from person to person. Sharing personal items like towels, nail clippers, and shoes can transmit the fungi. Furthermore, once one nail is infected, the fungus can spread to other nails.
Environmental Factors
Humid and warm environments contribute significantly to the development of fungal infections. People living in tropical climates or those who wear heavy, non-breathable shoes are at a higher risk.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination and may include laboratory tests to identify the specific type of fungus. Treatment options include antifungal medications, either topical or oral, and in severe cases, nail removal. However, treatment can be lengthy and challenging, and reinfection is common.
Prevention
Preventive measures include maintaining good hygiene, keeping nails short and dry, avoiding walking barefoot in public areas, using antifungal sprays or powders, and not sharing personal nail care items.
In conclusion, nail fungal infections are caused by an overgrowth of fungi in suitable environments. Understanding the risk factors and transmission methods is essential in preventing and effectively managing these infections. Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial for successful outcomes.




